|
Surgery
Because liver cancer is a "silent" disease, it is usually too advanced at the time of diagnosis to be removed completely by surgery. However, if detected early enough, and found to be in just one part of the liver, surgeons may remove one of the liver's two lobes, or they may remove a small portion, known as a segment. If there are a number of small tumors in different parts of the liver, the surgeon may remove the segments in which those tumors are located. Because the liver is one of the few human tissues able to regenerate very quickly, quite a large amount of liver can be removed without destroying the organ or harming its function. However, if the tumors are near major blood vessels they cannot be removed because the blood vessels may be damaged.
Cyrosurgery
Cyrosurgery is a method of selectively destroying tissue by freezing it with liquid nitrogen and leaving it in place to be reabsorbed by the body, rather than cutting it out. It is useful when tumors are in places where cutting the tumor out would damage surrounding vital structures such as blood vessels. So far, surgeons are finding this method as effective as actually cutting out the tumor. Surgeons operating to remove liver tumors may cut out some and freeze others at the same time, ensuring as much tumor as possible is removed.
Chemothorapy
Chemothorapy, a form of treatment where drugs highly toxic to growing cells are given either via the bloodstream (intravenously) or as pills (orally), is used to treat liver cancer which cannot be surgically removed. It is often given after surgery to destroy any cancer cells that may remain in the liver. Because chemotherapy drugs are toxic to rapidly growing cells, other cells including normal liver cells, red blood cells and immune cells are destroyed, so doses have to be limited or given in ways able to minimize this problem. Sometimes chemotherapy drugs are put directly into the liver, through a tube inserted into a liver artery, during surgery. This is done to give the tumor the highest dose possible without exposing too much of the rest of the body to these very toxic chemicals.
Chemo-embolization:
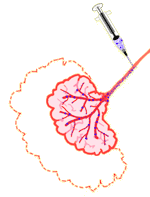
Emboli are small clumps of cells, fat, tissue, blood platelets or foreign bodies that flow through arteries and veins and eventually block them. If you inject little emboli into the arteries and veins supplying blood to a tumor, the tumor will lose its food and oxygen supply and die. Chemo-embolization is a technique now being used to destroy multiple tumors where small pieces of material saturated with chemotherapy drugs are injected into the arteries known to supply tumors. This works two ways. The blood flow supply is stopped and the tumor is left in a bath of highly toxic drugs, so it dies rapidly. This is still being tested as a form of therapy, but early studies indicate this method can shrink tumors in people with primary liver cancer and prolong their survival times.
 |
Blood vessels supplying food and oxygen to the tumor. |
| Creating an embolus or "blockage" using fat/tissue blood platelets and chemotherapy drugs cuts off the blood supply to the tumor and helps kill it. |
 |
Alcohol Injection:
Pure alcohol (100 percent alcohol) is highly toxic to liver tumors. When alcohol, usually ethanol, is injected directly into liver tumors, it makes the cells dry out and causes their protein to disintegrate. This form of treatment may be given to people who are considered medically unfit for surgery but who have only a few tumors. It has been found to increase survival significantly. Some hospitals are now experimenting with injecting the tumors with a mixture of alcohol and chemotherapy drugs to see if this is even more effective.
Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy is a common form of cancer treatment where a beam of radiation able to destroy cells is aimed at a tumor. It is not used very much in liver cancer because it is hard to protect the highly sensitive normal liver cells from the radiation. Sometimes a dose of radiation therapy may be given at the time of surgery to kill off any microscopic tumor cells the surgeon cannot see, in order to maximize clearance of the tumor.
Radio frequency ablation:
This is a new form of treatment, where tumor cells are literally "cooked" and therefore killed, by heating them to high temperatures, (80 - 100 oC). A thin needle is inserted through the skin and into the tumor using ultrasound to guide the operator. Once the needle is in the tumor, an electrical current is switched on, making the needle tip intensely hot, so it heats up and destroys the tumor. Small tumors less than four centimeters can be destroyed this way. Some advantages of this technique are that patients do not need general anesthetic, rarely have side effects and can usually go home soon after the procedure.
A similar technique using optical fibers instead of needles, known as interstitial laser photocoagulation, is also being tested now.
Liver Transplantation
This is only recommended for people with early stage primary liver cancer who have liver failure. The entire liver is removed and a healthy liver, usually donated by a car accident victim, is transplanted in its place. In the right cases, it can be an effective cure, as long as the cause of the liver failure i.e. alcohol abuse or hepatitis B infection has been treated effectively.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is a form of therapy that tries to enlist the body's immune system to fight cancer. It is currently experimental but involves taking materials taken from the patient's body, or making materials known as "biological response modifiers", and trying to use them to strengthen and direct the body's immune system to help it attack the cancer cells. |
| |
|
|
In TCM, liver cancer is mainly treated according to the classification of the individuals' disharmony pattern.
1. Spleen Deficiency
The therapeutic aim is to strengthen the spleen. This decoction example includes the four herbs, which are a well-known combination for boosting spleen health and spleen qi in the body:
Si Junzi Decoction
| Dang shen |
Tangshen |
| Bai Zhu |
Largehead Atractylodes Rhizome |
| Fu Ling |
Indian Bread |
| Gan Cao |
Liquorice Root |
In this decoction, dang shen invigorates qi. Bai zhu strengthens the spleen. Fu ling promotes diuresis (urination) to eliminate dampness, and Gan Cao moderates the other herbs.
Modification may be made to the basic Si Junzi decoction in order to promote the regulation of qi. An example includes:
Xiangsha Liujun pills
| Dang shen |
Tangshen |
| Bai Zhu |
Largehead Atractylodes Rhizome |
| Fu Ling |
Indian Bread |
| Gan Cao |
Liquorice Root |
| Ban xia |
Pinellia Tuber |
| Chen pi |
Dried Tangerine Peel |
| Mu xiang |
Costusroot |
| Sha ren |
Villous Amomum Fruit |
In this decoction, the basic four herbs in Si Junzi Decoction help strengthen the spleen. In addition, Ban xia and Chen pi regulates qi circulation and eliminates dampness and phlegm. Mu xiang and Sha ren further promote the qi circulation. The decoction is especially good for patients with spleen deficiency and stagnation of qi.
2. Abdominal distention (ascites)
Xiangsha Liujun pills can further be modified to treat abdominal distention. Modification is as follows.
| Dang shen |
Tangshen |
| Bai Zhu |
Largehead Atractylodes Rhizome |
Fu ling
(outer cortex) |
Indian Bread Peel |
| Gan Cao |
Liquorice Root |
| Ban xia |
Pinellia Tuber |
| Chen pi |
Dried Tangerine Peel |
| Mu xiang |
Costusroot |
| Sha ren |
Villous Amomum Fruit |
| Che qian zi |
Plantain Seed |
| Da fu pi |
Areca Peel |
In addition to the benefits of treating spleen deficiency and qi stagnation, the decoction also contains Che qian zi and Da fu pi, which can further relieve stagnation, promote diuresis (urination) and relieve edema (swelling) and dampness.
3. Stagnation of qi
The therapeutic aim is to resume the circulation of qi in the middle burner including the stomach and spleen.
Zhishi Xiaopi Pills
| Dang shen |
Tangshen |
| Bai Zhu |
Largehead Atractylodes Rhizome |
| Fu Ling |
Indian Bread |
| Gan jiang |
Dry Ginger |
| Ban xia qu (one type of Ban xia) |
PinelliaTuber |
| Zhi shi |
Immature Orange Fruit |
| Hou po |
Officinal Magnolia Bark |
| Huang liang |
Golden Thread |
| Mai ya |
Germinated Barley (fried) |
In this decoction, Zhi shi is the main herb for promoting qi circulation, dispersing the stagnation and helping to remove the abdominal mass. It is further supported by Hou po. Both Ban xia and Gan jiang are pungent in taste. In TCM, pungent tasting herbs can be used to help to remove a mass. Chinese terms describe this as "opening" the mass. Huang liang has bitter and cold properties that can clear away heat and remove dampness. Together with the bitter taste of Zhi shi and Hou po, they descend the qi, which also helps to disperse the mass. The whole decoction is supported by Dang shen, Bai zhu, Fu ling, which are all good herbs in invigorating spleen and removing dampness.
4. Influence of dampness and heat
Yinchenhao Decoction
| Yin chen |
Virgate Wormwood Herb |
| Zhi zi |
Cape Jasmine Fruit |
| Da huang |
Rhubarb |
In the decoction, Yin chen is the main herb for clearing away heat and dampness and relieving jaundice. Zhi zi has cold and bitter properties, which eliminates heat and guides the dampness and heat to move downwards by penetrating the triple burner meridian. In TCM, the triple meridian is regarded as the distribution channels for body fluids. Da Huang is also cold and bitter. Not only can it remove heat, dampness and stasis, but is especially helpful in guiding the heat to leave the body through stools by penetrating the large intestine meridian.
5. Excessive heat
Baihu Decoction
| Shi gao |
Gypsum |
| Zhi mu |
Common Anemarrhena Rhizome |
| Gan Cao |
Liquorice Root |
In this decoction, both Shi gao and Zhi wu are cold herbs. Shi gao is also pungent and sweet. The decoction is very useful for removing extreme heat in the body, and it is supported by the Zhi wu herb, which is also cold and bitter. Gan cao is essential for protecting the stomach and spleen, and preventing the cold herbs from hurting the spleen. The decoction also has the added benefit of nourishing the body's yin.
6. Blood stasis
Shixiao powder
| Pu huang |
Cattail pollen |
| Wu ling zhi |
feces of Trogoterus xanthipes |
In this decoction, both Pu huang and Wu ling zhi promote blood circulation, remove blood stasis and relieve pain.
7. Yin deficiency
Sancai decoction
| Taizi shen |
Heterophylly Falsestarwort Root |
| Tian dong |
Cochinchinese Asparagus Root |
| Sheng di |
Rehmannia Root |
In this decoction, Taizi shen is good for invigorating qi and promoting the production of body fluids. All three herbs work together to replenish yin deficiency in the body. Tian dong nourishes yin, clears away heat, moisturizes the lungs and benefits the kidneys. Sheng di cools the blood and nourishes yin to promote the production of body fluids.:
|
| |
|