 |
| Traditional TCM drawing of organ placement |
Criteria to diagnose impotence are similar in both Chinese and Western medicine. Impotence is defined as inability to obtain penile rigidity to permit coitus for adequate duration, and the situation lasts for at least three months subsequently. During consultation, the TCM physician employs four basic techniques (questioning, smelling / listening, palpation and inspection) to evaluate the patient's health state. Based on gathered clinical information, the physician analyzes the existing symptoms and diagnoses an individualized TCM syndrome pattern. This is the most crucial process, which requires experience in collecting clinical data and skillful synthesis of a comprehensive syndrome pattern. Once this is accomplished, the appropriate treatment can be determined. The following are typical symptom patterns in impotence. It should be emphasized that in reality, people usually have a mixed type.
|
1. Debility of vital gate fire
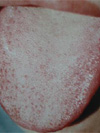 |
| Tongue covered with white fur. |
Individuals present with symptoms of impotence, a decline in libido, weakness and soreness in lumbar area (lower back) and knees, aversion to coldness, cold extremities, dizziness, apathy, a pale face and clear and profuse urine.
On examination, the tongue is pale and covered by a white fur; the pulse is deep, thready and weak. |
| |
|
|
2. Fear damaging the kidneys
Most of the individuals either have some serious fear or have had frightening experiences. Besides impotence, other symptoms of timidness, vexation, amnesia, dizziness, lower back pain and tinnitus (ear ringing) may be present.
On examination, the tongue is pale covered by thin and greasy fur; the pulse is taut and thready. |
| |
|
|
3. Stagnation of liver-qi
Individuals are usually depressed or manic and irritable. They prefer to sigh and feel discomfort in hypochondriac areas (upper lateral regions of the abdomen, below the ribs) and may have chest oppression, impotence and loss of libido.
On examination, the tongue is pale red and covered with thin fur; the pulse is taut. |
| |
|
|
4. Spleen and heart deficiency
Besides impotence, individuals experience symptoms of fatigue, lusterless complexion, loss of appetite, heart palpitations, insomnia and loose stools.
On examination, the tongue is pale and covered with white fur; the pulse is thready and weak. |
| |
|
|
5. Downward accumulation of dampness-heat
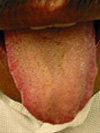 |
| Tongue covered with yellow and greasy fur. |
Individuals present with a flaccid penis and may experience a bearing down sensation and distention or a burning pain in one or both testes. The surface area of the scrotum may appear moist. The lower limbs are weak and sore and there is scanty or dark brown urine output. The person may fidget and have a bitter taste in the mouth.
On examination, the tongue is red, covered by a yellow and greasy fur; the pulse is rolling and rapid. |
| |
|
|
6. Obstruction from blood stasis
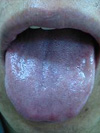 |
| The tongue has a purple color. |
Besides impotence, individuals can present with symptoms of a prickling pain in the testes and pain or distended feelings in the chest and hypochondria (upper lateral regions (left and right) of the abdomen, below the ribs). Sometimes the prickling pain may also appear in the lower back, abdominal or perineum areas. The individual also may appear fidgety and has a tendency to anger easily.
On examination, the tongue is purplish in color or may have a bruised appearance; the pulse is thready and hesitant.
The table below provides a general reference about the Western classifications of impotence and the corresponding TCM syndrome patterns.
Western Medicine |
TCM Syndrome Patterns |
| |
|
|
Fear and fright damaging the kidneys |
|
|
Spleen and heart deficiency |
|
|
Stagnation of liver-qi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Downward accumulation of dampness-heat |
|
|
Obstruction by phlegm-dampness |
|
|
Obstruction by blood stasis |
|
| |
3. Iatrogenic (A secondary condition caused by medical activity.) |
|
|
|
Obstruction by blood stasis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Debility of the vital gate fire |
|
|
Kidney yin deficiency |
|
|
Kidney yang deficiency |
|
|
|